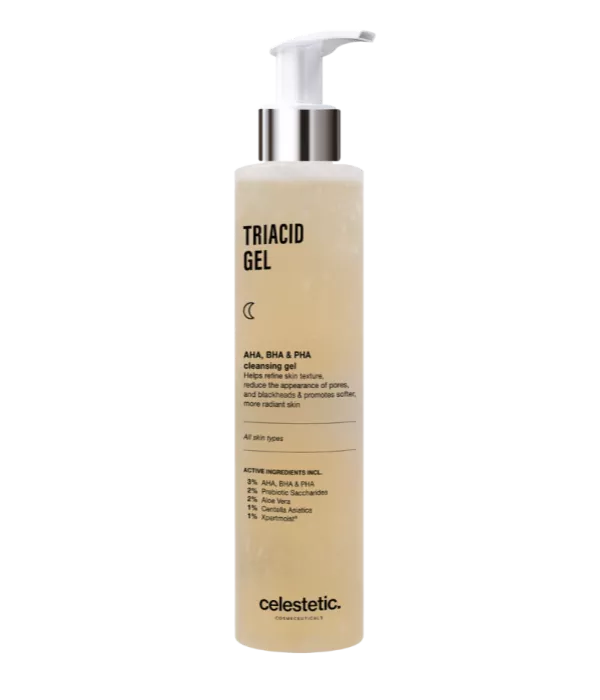
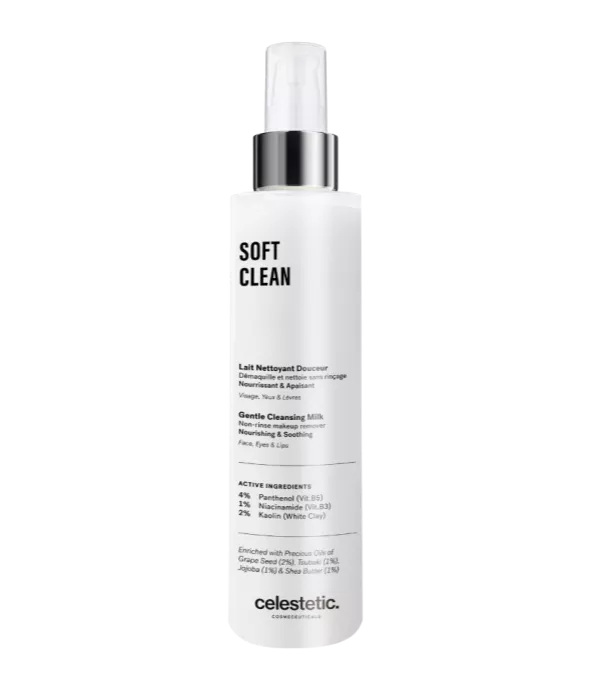
Its mode of action

Aloe Vera has several modes of action
The healing properties are due to the polysaccharides and gibberellin, a growth hormone, contained in aloe vera. They stimulate the activity of fibroblasts, which synthesize collagen. Thanks to this, aloe vera accelerates wound contraction. In addition, aloe increases the concentration of hyaluronic acid and dermatan sulfate in the scar tissue, essential elements for healing.
The moisturizing properties of aloe vera are due to the fact that the gel can penetrate all layers of the epidermis. It contains more than 70 potential active natural substances (vitamins, enzymes, minerals, sugars, lignin, saponins, salicylic acids and amino acids) that improve blood circulation.
The gel promotes the production of fibroblasts. Fibroblasts are present in the dermis where they produce extracellular matrix components such as collagen fibers and elastin. This regenerates skin cells and allows it to remain elastic and fight the signs of aging (wrinkles).
Aloe vera has soothing properties. It inhibits the cyclooxygenase pathway and reduces the production of prostaglandin E2.